Wireshark
Packet Filtering
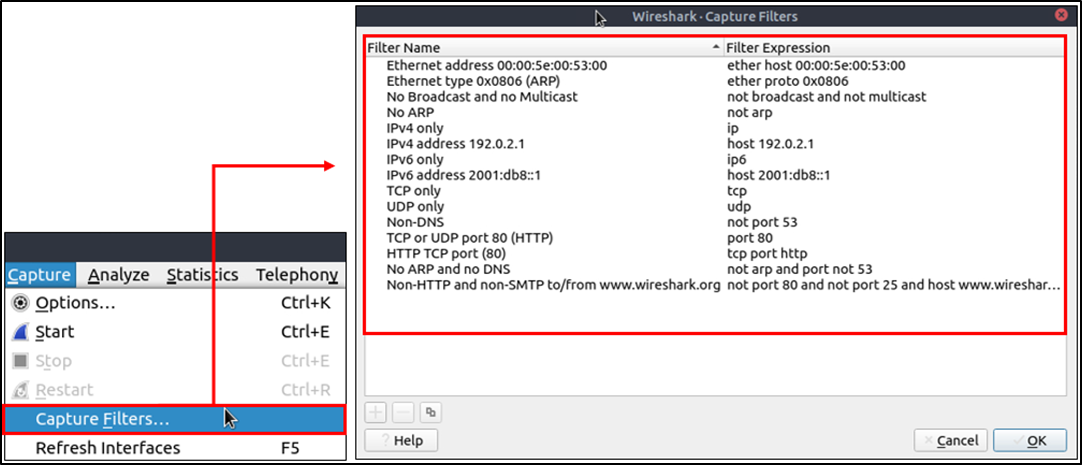
Capture Filter Syntax
These filters use byte offsets hex values and masks with boolean operators, and it is not easy to understand/predict the filter’s purpose at first glance. The base syntax is explained below:
- Scope: host, net, port and portrange.
- Direction: src, dst, src or dst, src and dst,
- Protocol: ether, wlan, ip, ip6, arp, rarp, tcp and udp.
- Sample filter to capture port 80 traffic: tcp port 80
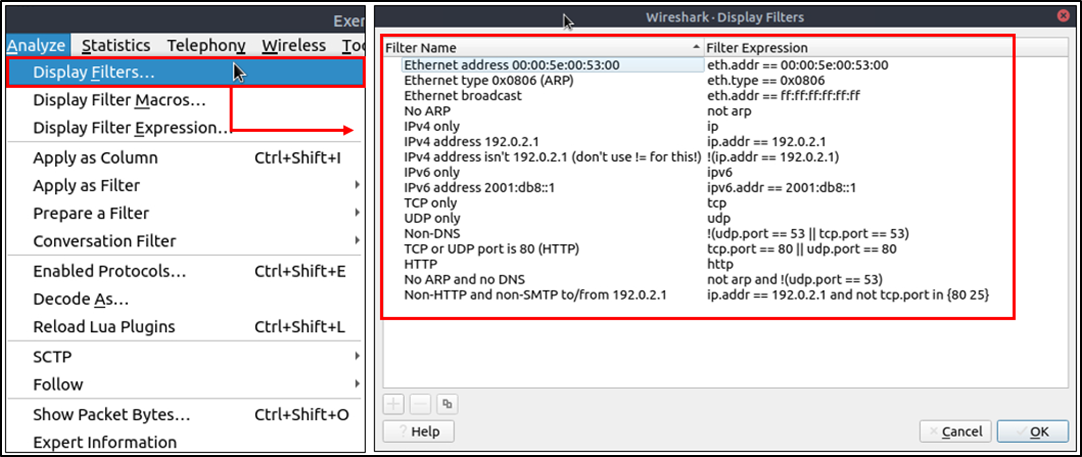
Display Filter Syntax
Sample filter to capture port 80 traffic: tcp.port == 80 A quick reference is available under the “Analyse –> Display Filters” menu.
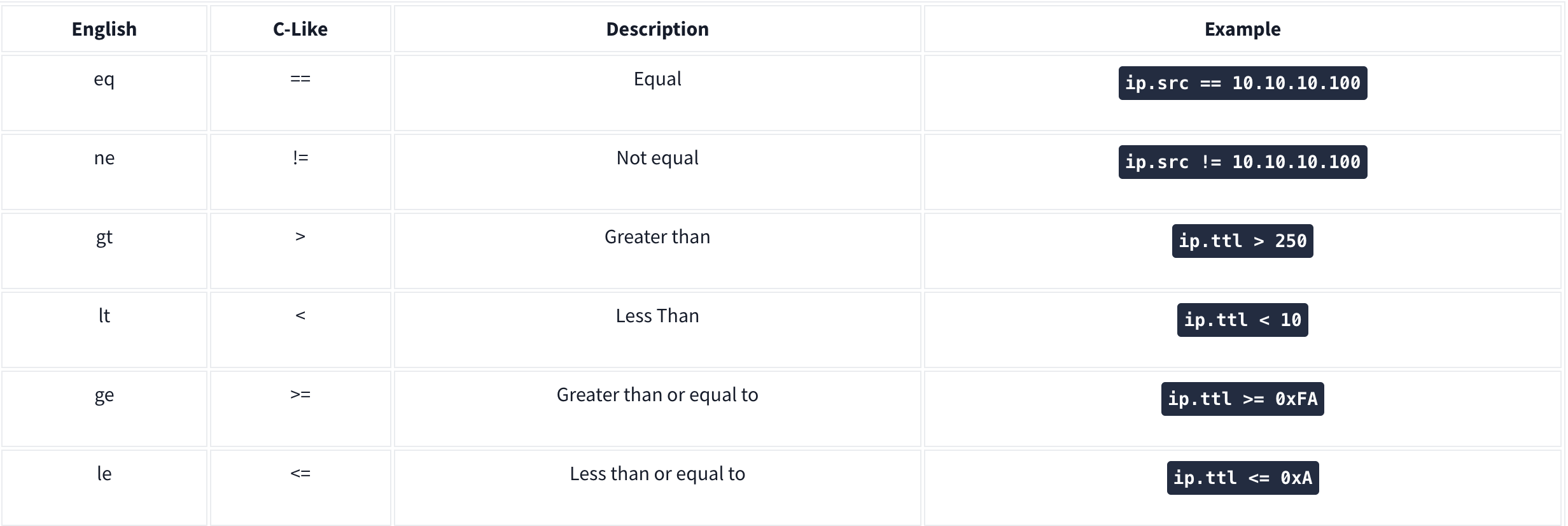
Comparison Operators
You can create display filters by using different comparison operators to find the event of interest. The primary operators are shown in the table below.
Note: Wireshark supports decimal and hexadecimal values in filtering. You can use any format you want according to the search you will conduct.
Logical Expressions
Wireshark supports boolean syntax. You can create display filters by using logical operators as well.
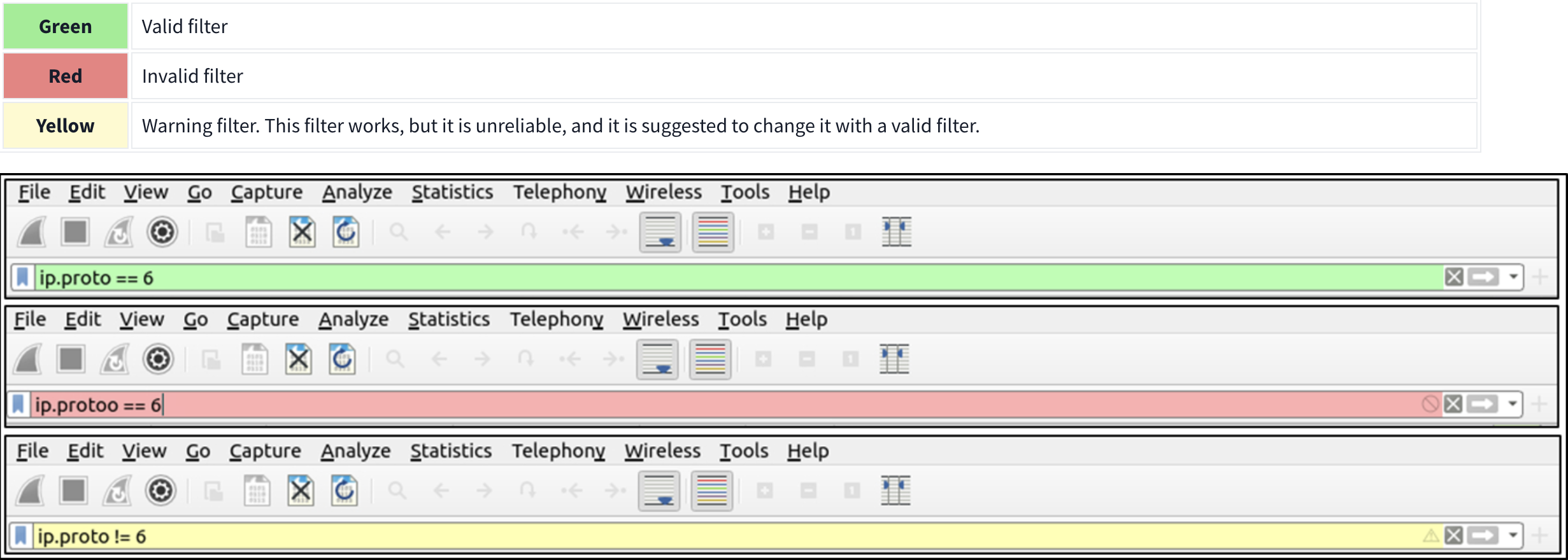
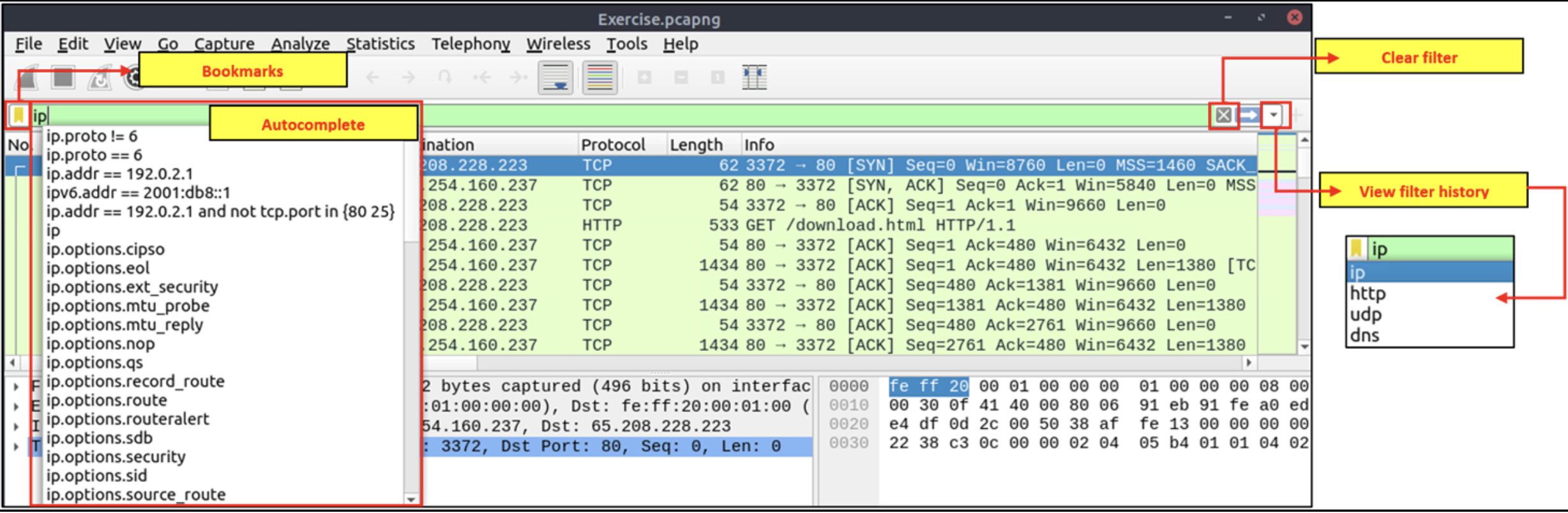
Packet Filter Toolbar
The filter toolbar is where you create and apply your display filters. It is a smart toolbar that helps you create valid display filters with ease. Before starting to filter packets, here are a few tips:
- Packet filters are defined in lowercase.
- Packet filters have an autocomplete feature to break down protocol details, and each detail is represented by a “dot”.
- Packet filters have a three-colour representation explained below.
Filter toolbar features are shown below.
Protocol Filters
Wireshark supports 3000 protocols and allows packet-level investigation by filtering the protocol fields. This task shows the creation and usage of filters against different protocol fields.
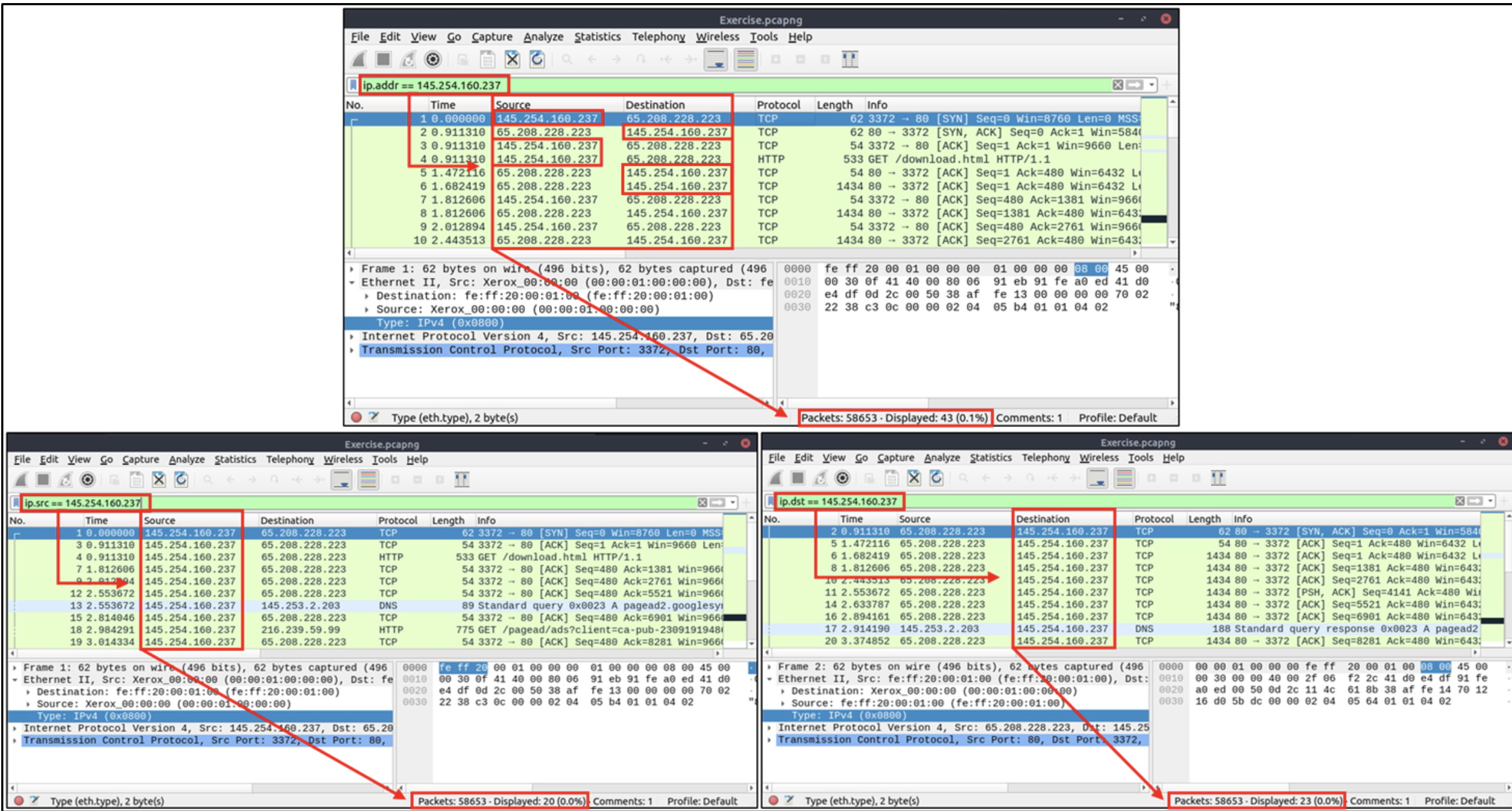
IP Filters
IP filters help analysts filter the traffic according to the IP level information from the packets (Network layer of the OSI model). This is one of the most commonly used filters in Wireshark. These filters filter network-level information like IP addresses, version, time to live, type of service, flags, and checksum values.
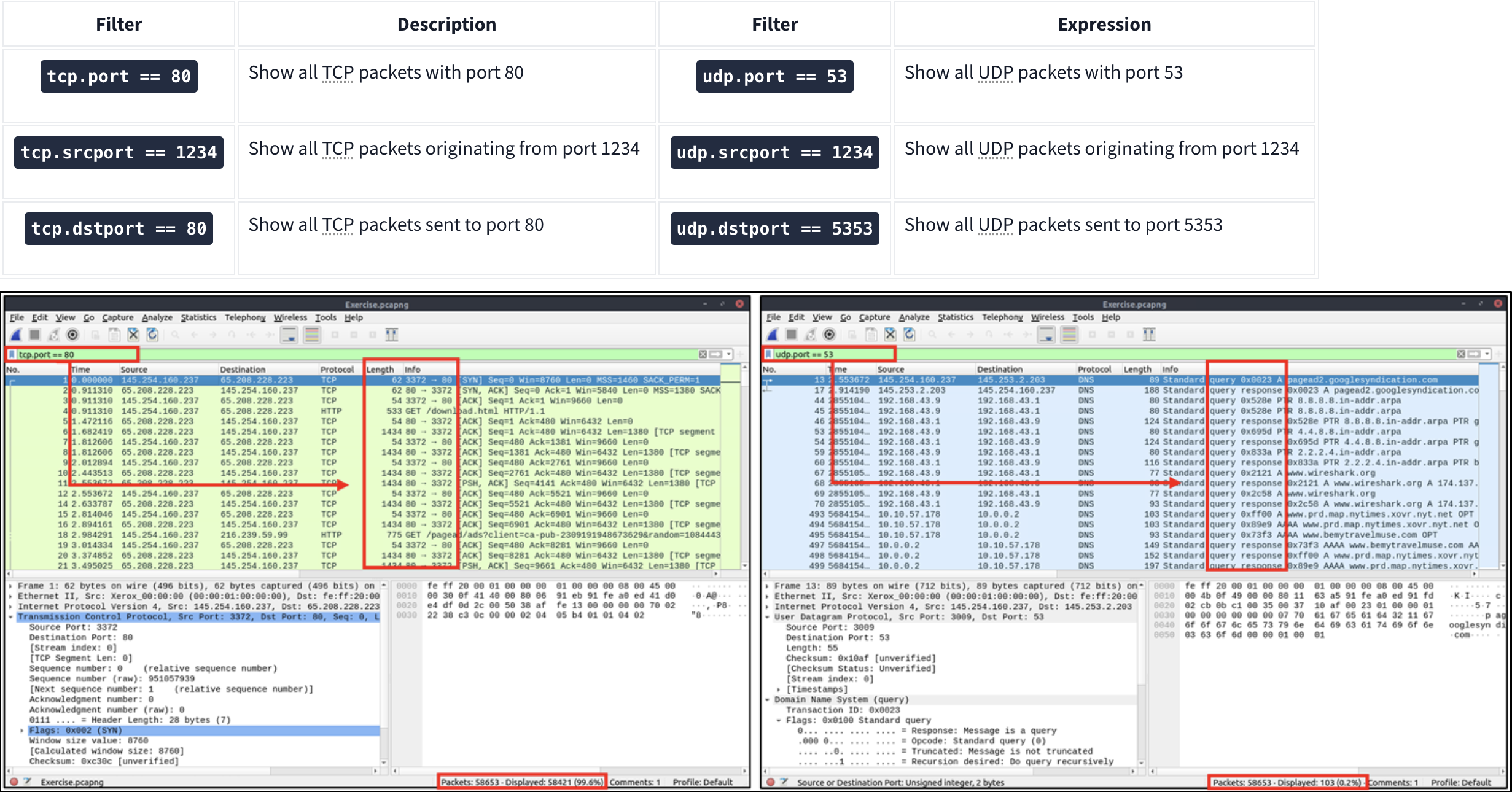
TCP and UDP Filters
TCP filters help analysts filter the traffic according to protocol-level information from the packets (Transport layer of the OSI model). These filters filter transport protocol level information like source and destination ports, sequence number, acknowledgement number, windows size, timestamps, flags, length and protocol errors.
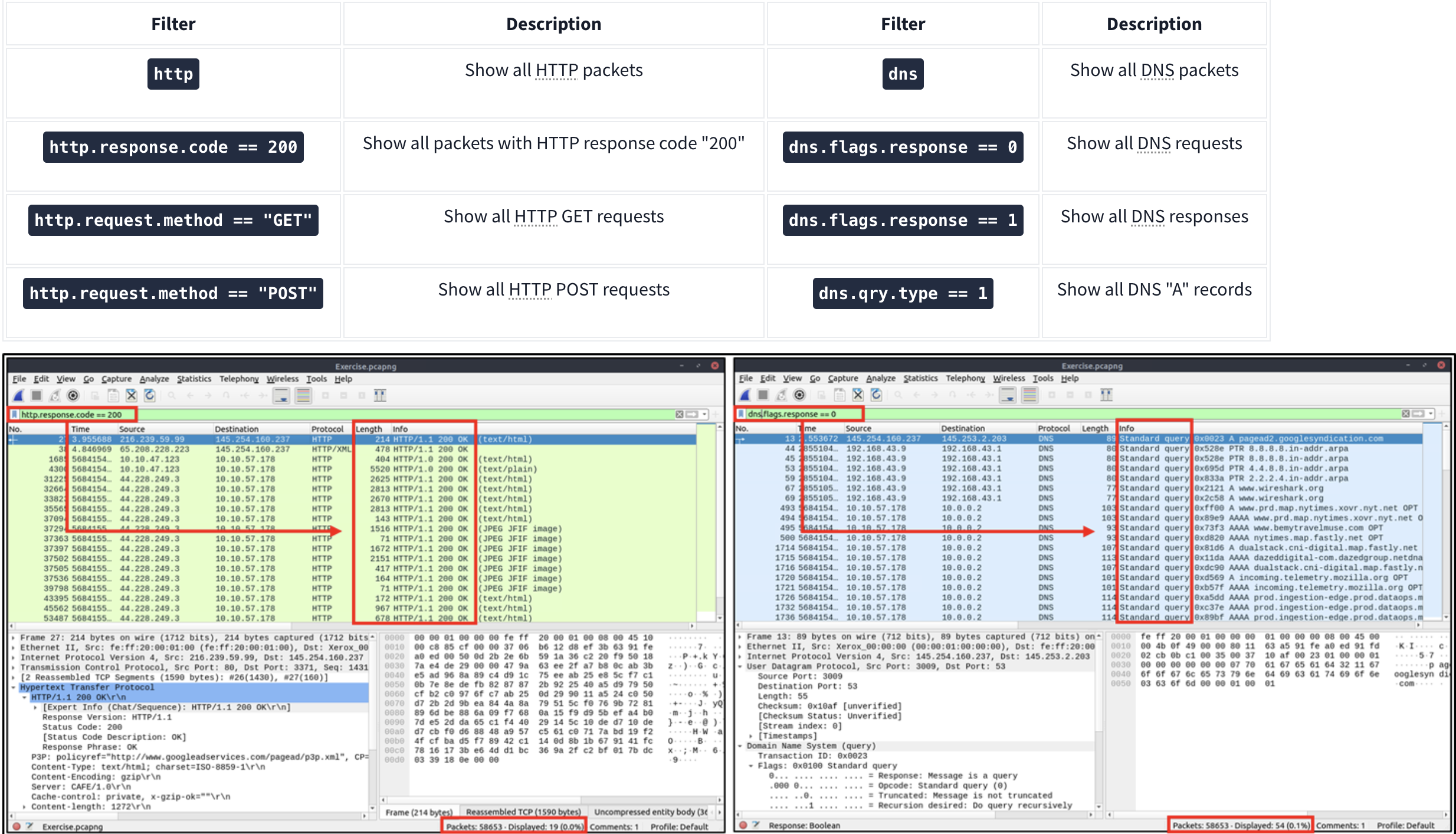
Application Level Protocol Filters | HTTP and DNS
Application-level protocol filters help analysts filter the traffic according to application protocol level information from the packets (Application layer of the OSI model ). These filters filter application-specific information, like payload and linked data, depending on the protocol type.