Ramnit Blue Team Lab
Summary Introduction:
In this memory analysis report, we delve into the identification and investigation of a suspicious process detected within the system’s memory. By leveraging the Volatility framework, we meticulously examine running processes to pinpoint any irregularities. Initially, we identify the suspicious process, “ChromeSetup.exe,” using Volatility’s process listing command and then we trace its file path and uncover its network connections to understand its communication strategy. Further investigation involves dumping the malware and analyzing its hash to ascertain its threat level. Lastly, VirusTotal analysis confirms the severity of the malware, highlighting its potential dangers and aiding in preemptive security measures.
Getting the image information
Using the command volatility -f memory.dmp window.info
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
Variable Value
Kernel Base 0xf80049400000
DTB 0x1ad000
Symbols file:///opt/forensics/volatility3/volatility3/symbols/windows/ntkrnlmp.pdb/68A17FAF3012B7846079AEECDBE0A583-1.json.xz
Is64Bit True
IsPAE False
layer_name 0 WindowsIntel32e
memory_layer 1 WindowsCrashDump64Layer
base_layer 2 FileLayer
KdDebuggerDataBlock 0xf8004a000b20
NTBuildLab 19041.1.amd64fre.vb_release.1912
CSDVersion 0
KdVersionBlock 0xf8004a00f398
Major/Minor 15.19041
MachineType 34404
KeNumberProcessors 4
SystemTime 2024-02-01 19:54:11
NtSystemRoot C:\Windows
NtProductType NtProductWinNt
NtMajorVersion 10
NtMinorVersion 0
PE MajorOperatingSystemVersion 10
PE MinorOperatingSystemVersion 0
PE Machine 34404
PE TimeDateStamp Wed Jun 28 04:14:26 1995
Indetification of the suspicious process
We need to identify the process responsible for this suspicious behavior. What is the name of the suspicious process?
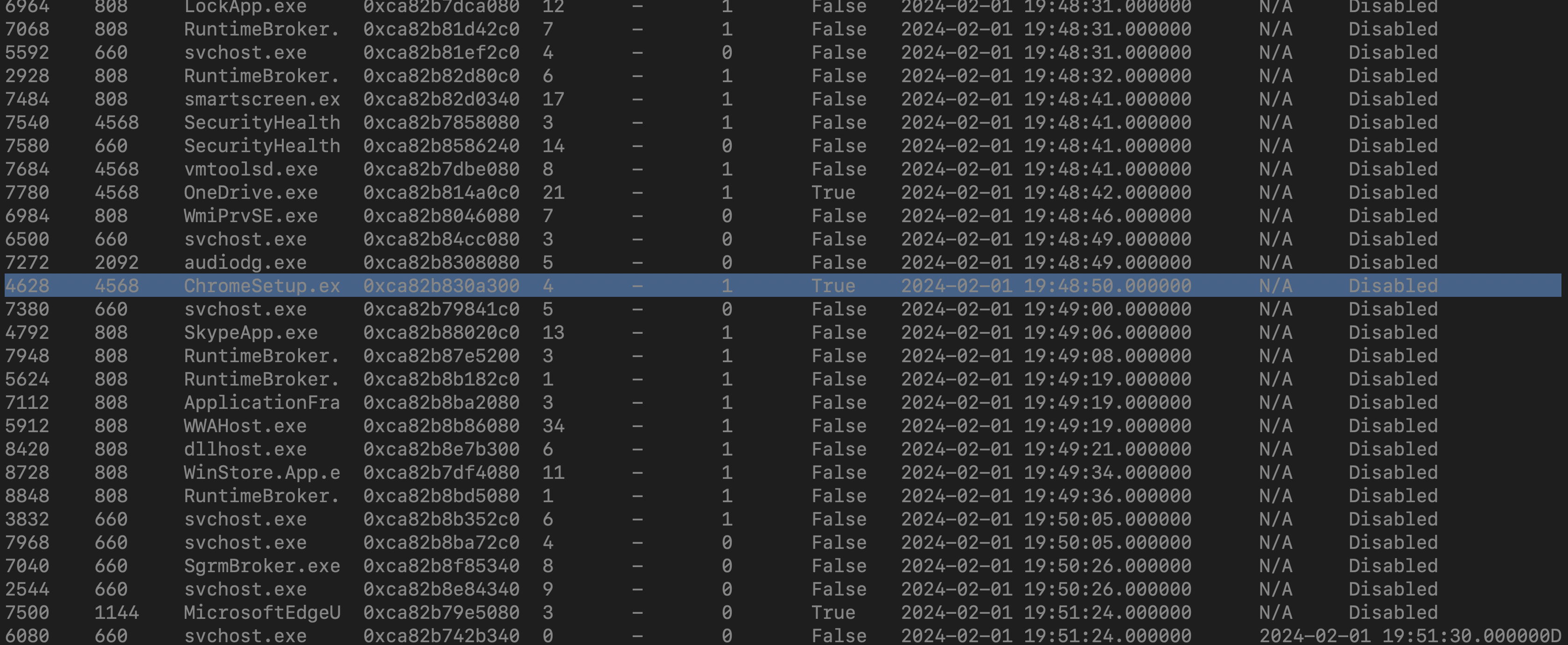
Utilizing the volatility framework with the command volatility -f memory.dmp windows.pslist, we aim to extract a comprehensive list of running processes during the memory dumping process. This allows for a meticulous examination of each process to discern any irregularities or potential threats.
and chrome seems to be the one standing out
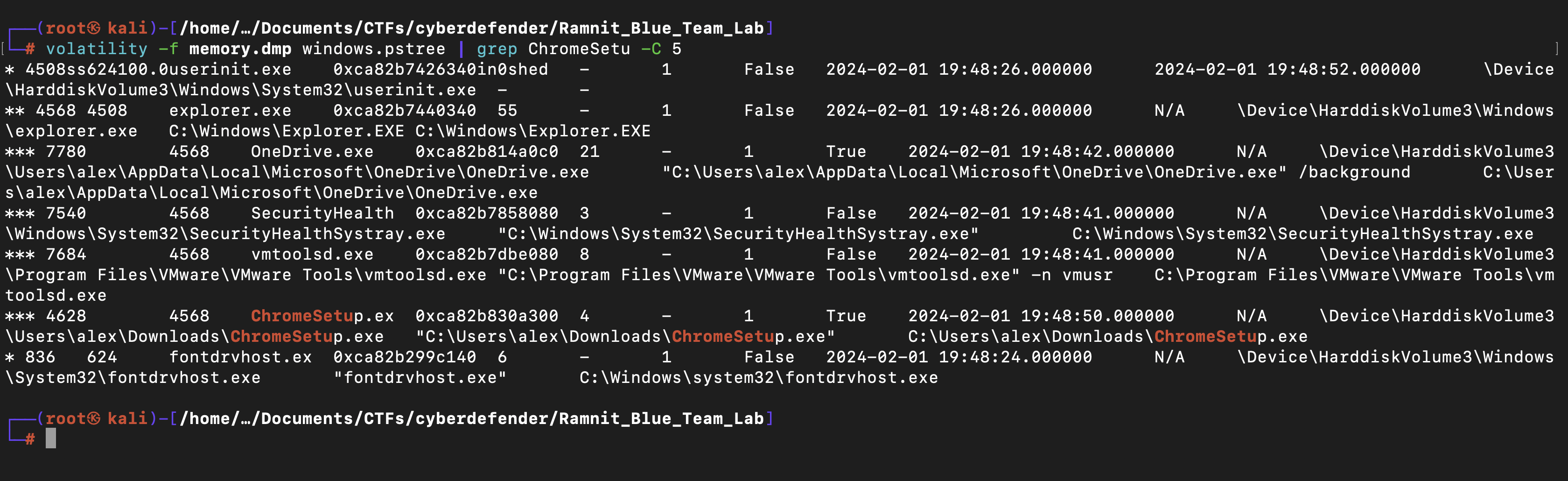
Getting the file path of the suspicious process
To figure out where the suspicious process is located, we’ll use another command: volatility -f memory.dmp windows.pstree | grep ChromeSetu -C 5.
It turns out the file is located at C:\Users\alex\Downloads\ChromeSetup.exe
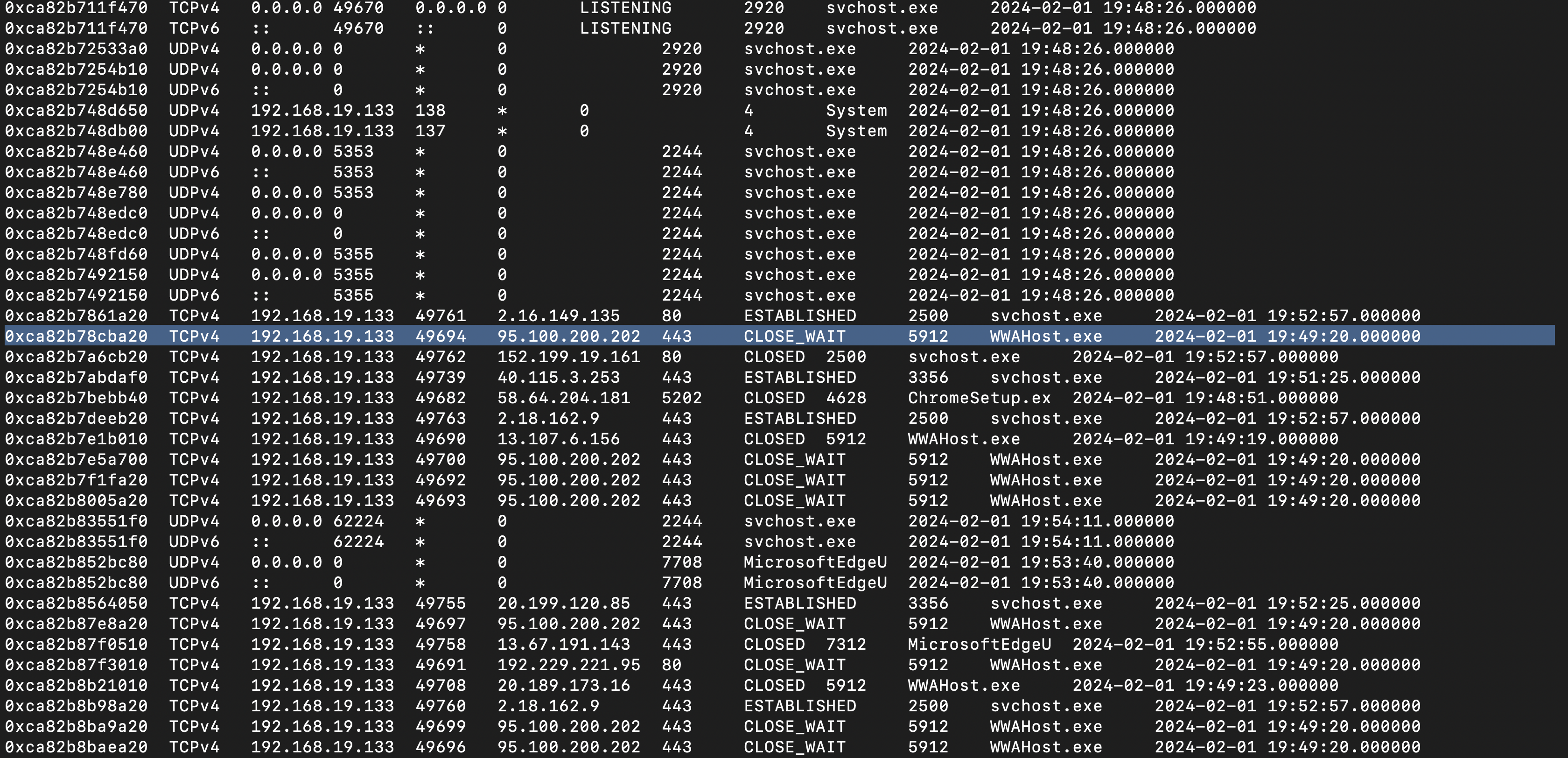
Identifying the network connections(IP addresses and ports)
Understanding how the malware is communicating is important. We’ll use volatility -f memory.dmp windows.netscan to find out which IP address it’s trying to connect to.
Once we have the IP address, we can use tools like iplocation to see where the attacker might be.
Further investigation
Now that we know the PID of the malware, we can dig deeper. We’ll dump the malware using volatility -f memory.dmp windows.dumpfiles --pid 4628 and get its hash.
1
2
3
┌──(root㉿kali)-[/home/…/CTFs/cyberdefender/Ramnit_Blue_Team_Lab/dumped]
└─# sha1sum file.0xca82b85325a0.0xca82b7e06c80.ImageSectionObject.ChromeSetup.exe.img
280c9d36039f9432433893dee6126d72b9112ad2 file.0xca82b85325a0.0xca82b7e06c80.ImageSectionObject.ChromeSetup.exe.img
Vurus total
We’ll submit the hash to VirusTotal to see what it says. Turns out, it’s a very dangerous malware, and lots of security programs are flagging it 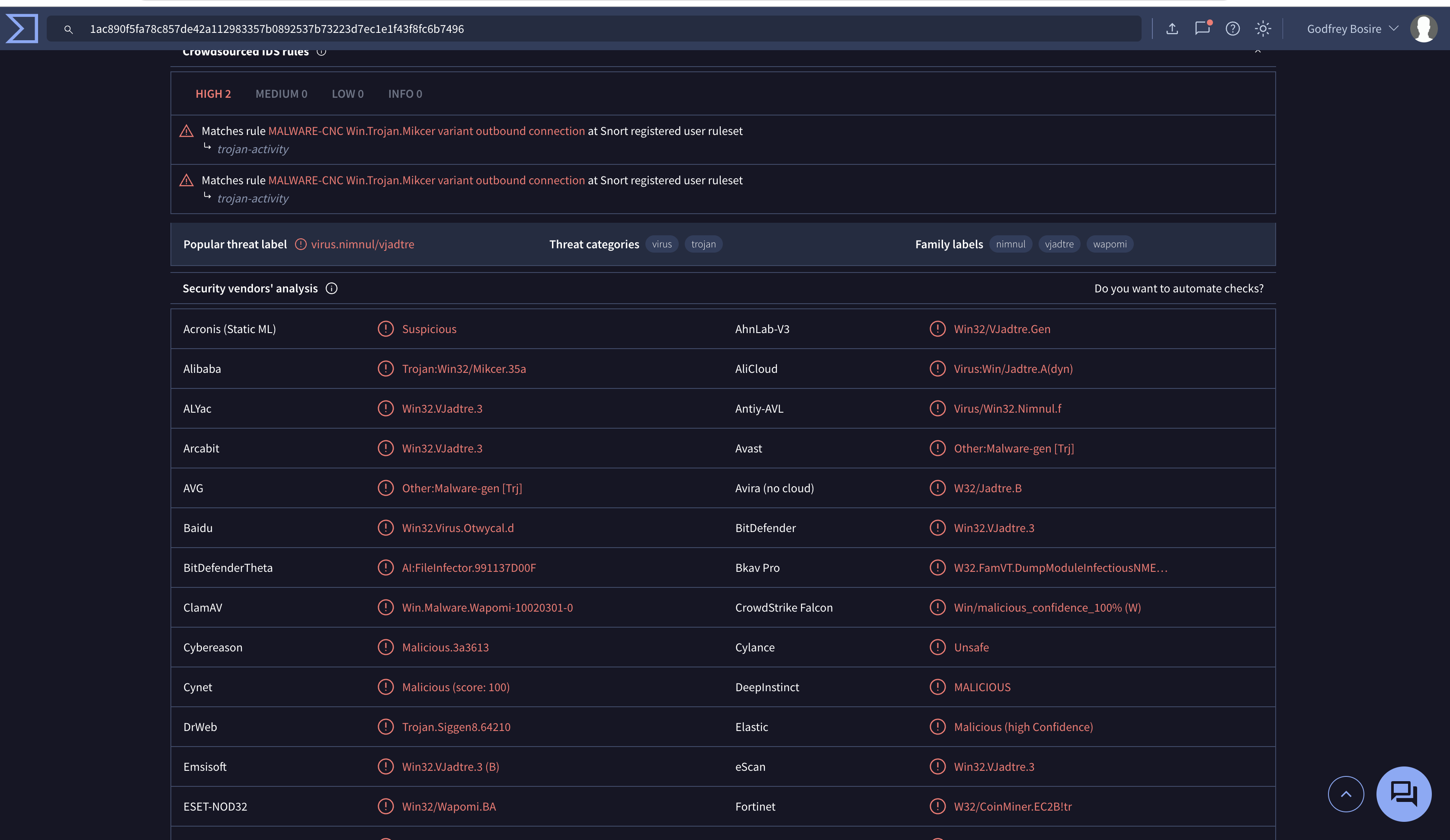
VirusTotal also tells us when the malware was first seen (2024-02-03 00:02:57) and shows us domains linked to this malware, which helps us stop similar attacks in the future.